FAQ
Please review our frequently asked questions below:
How does 3d printing affect the look of the shell?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, can have a significant impact on the final appearance of products.
Additive manufacturing actually comes in multiple forms depending on the type of technology used. VEYL uses the most common and simplest method, Fused Deposition Modeling or FDM. Two main visual properties as a result of this process are the creation of horizontal layers and vertical seams which mark the beginning and end of a layer.
Horizontal Layers
FDM prints each part in thin horizontal layers, at certain predefined layer heights. The graphic below demonstrates that given a curved portion of a product, a series of horizontal lines are sequentially printed to fit the end product design as closely as possible. These layers are typically less than half of a millimeter in height, meaning for larger parts these layer lines are largely unnoticeable unless very closely inspected. All 3d printed products without major post processing will have these layers to varying degrees.
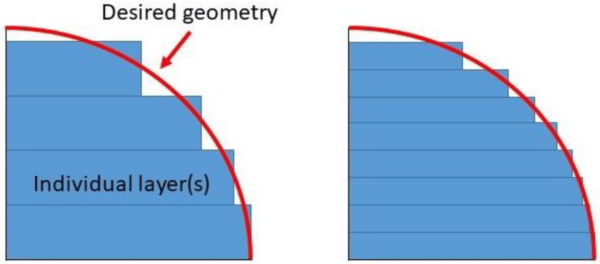
All 3d prints using the FDM method produces thin, horizontal stacking layers to produce geometry.
Seams
The other major aspect of FDM printing are seams. They are exactly what they sound like, which is a slight visual indent in the product where the layer extrusion begins and ends. There are many tricks and methods used to make them less noticeable and hidden, but they are a necessary feature of this 3d printing method and should be expected.
VEYL designs are produced to minimize seams as much as possible and hide within the textures of the product.
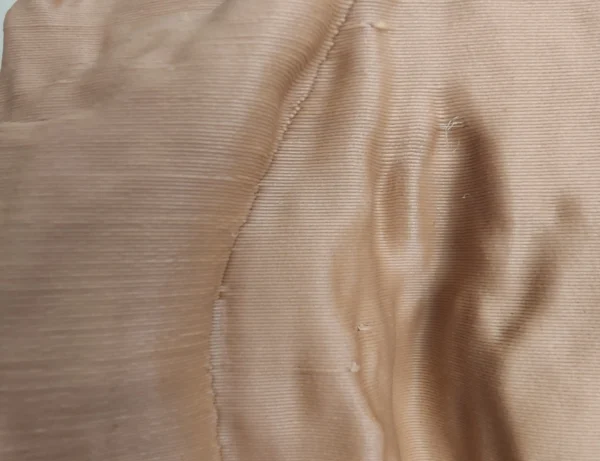

Pictured above is an example of our VEYL Wood shell seam hiding along a vertical fold.
Why use additive manufacturing vs traditional methods?
Crafting furniture has long been a complex and intricate process where traditional furniture making techniques continue to encounter common challenges:
- Labor Intensive
- Furniture crafting typically involves human labor of at least some capacity to create a finished piece. This can be in the creation and forming of materials, or the process of assembling materials into a final form. Today in a globalized economy, this labor is typically offshored to countries with very low wages.
- Furniture crafting typically involves human labor of at least some capacity to create a finished piece. This can be in the creation and forming of materials, or the process of assembling materials into a final form. Today in a globalized economy, this labor is typically offshored to countries with very low wages.
- Limited Materials
- Wood is one of the most common sources of building material, but it can be expensive to import/export depending on the type of wood used. Higher quality wood suitable for furniture tends to come at a premium that is out of reach for the average consumer.
- Other materials can be used such as composites or metals, but there can be ambiguity on the sourcing for these materials with quality being an afterthought.
- Wood is one of the most common sources of building material, but it can be expensive to import/export depending on the type of wood used. Higher quality wood suitable for furniture tends to come at a premium that is out of reach for the average consumer.
- Lack of Innovation
- While there is nothing wrong with having custom made furniture from a craftsman or professional, the tools and methods have remained largely unchanged for hundreds if not thousands of years leading to the process being slow and time consuming.
- Newer manufacturing methods such as injection molding can create cost effective products, but often lack visual detail and have design limitations.
- Automated tooling such as CNC machines can partially reduce the labor needed, but they still rely on traditional reductive manufacturing methods and still need regular human operation and intervention.
- While there is nothing wrong with having custom made furniture from a craftsman or professional, the tools and methods have remained largely unchanged for hundreds if not thousands of years leading to the process being slow and time consuming.
The Benefits of Additive Manufacturing
- Non-Reductive
- Additive manufacturing produces products into its final shape from the ground up, which is the opposite of traditional manufacturing which cuts away material to a final shape from a stock piece. This allows for significant material cost savings and eliminates waste in the production process.
- Additive manufacturing produces products into its final shape from the ground up, which is the opposite of traditional manufacturing which cuts away material to a final shape from a stock piece. This allows for significant material cost savings and eliminates waste in the production process.
- Unbound Design Freedom
- One of the more exciting aspects of additive manufacturing is the ability to create complex and intricate designs that would be impossible or highly difficult using traditional methods. What once would take a master artisan many hours to create, a 3d printer can do effortlessly.
- One of the more exciting aspects of additive manufacturing is the ability to create complex and intricate designs that would be impossible or highly difficult using traditional methods. What once would take a master artisan many hours to create, a 3d printer can do effortlessly.
- Fully Automated
- Lets remove cost effective furniture being synonymous with cheap human labor. Additive manufacturing can create end use products from scratch without any human intervention.
- Lets remove cost effective furniture being synonymous with cheap human labor. Additive manufacturing can create end use products from scratch without any human intervention.
- Material Variety
- While VEYL specifically uses PLA, a sustainably sourced material, a 3d printer can actually utilize many different types of thermoplastics and metals depending on the need.
- While VEYL specifically uses PLA, a sustainably sourced material, a 3d printer can actually utilize many different types of thermoplastics and metals depending on the need.
- Local Production
- Perhaps the most underrated factor, additive manufacturing vastly makes it easier to produce products virtually anywhere. This drastically reduces the need to offshore labor and brings business logistics back to local economies.
How much assembly is actually required?
Similar to some of the most popular DIY brands today, we believe the most cost effective solution for customers is for them to assemble the furniture themselves from basic kits.
VEYL strives to make this incredibly easy with as few parts as possible. In fact, all kits and designs feature only 3 screws to hold everything together into a reliable, dependable product.
For detailed assembly instruction, please visit our Assembly Guide.
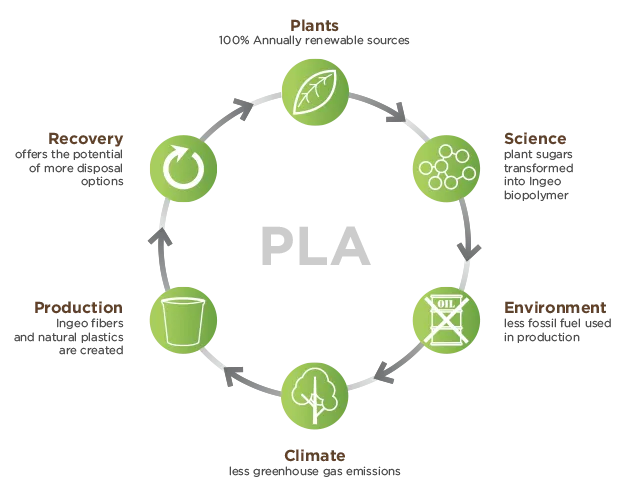
Tell me more about PLA plastic
As mentioned in our home page Sustainability section , PLA is derived from organic crops such as corn or sugarcane making it one of the most sustainable thermoplastic materials available. The graphic below provides some more detail on the process cycle for PLA:
Is it Biodegradable?
PLA is technically biodegradable, but there are some misconceptions to clear up on its compostable properties. For it to biologically degrade, certain industrial conditions such as temperatures being within 55-70ºC must be met where it can then degrade in a few months time. This means don’t throw printed PLA parts into the ground and expect it to degrade like food waste. Under more common conditions such as landfills, PLA can take decades to fully decompose.
Can it be recycled?
PLA itself can be recycled but unfortunately not at the consumer level by collection agencies due to the difficulty of identifying and processing the polymer. PLA scraps can be recycled at industrial levels, but this is out of reach for the average person. Recently, some U.S. based 3d printing companies are starting to do recycle programs for this issue, but it remains a limited service.
Our company hopes to reach the point where we can start offering PLA recycle programs, making VEYL a fully plastic waste-neutral product.
Is it safe for humans?
PLA has been shown to be non-toxic, thanks to it being derived from organic plant matter. In fact, its used in certain medical applications such as implants since the material can be safely absorbed in the body.
Like any material PLA has both strengths and weaknesses. Its sustainability is by far stronger that most other commercially available plastics, especially petroleum based ones, and its recyclability can be improved as adoption continues to grow.
What is the best way to clean a VEYL shell?
For light dirt stains or dust, we recommend using water with a mild soap to clean the PLA shells. For harder stains or grime, isopropyl alcohol can be used as well.
Do not use acetone to clean shell as this can severely degrade the PLA plastic.
Do not use hot water directly on shell as this can soften and deform the material.
I still have questions not found here
Please reach out using the Contact Us link.